
It doesn’t consider principal repayments or non-operating income fluctuations. A high ratio indicates that the company can easily cover its interest payments, implying lower financial risk. Utilize the TIE Calculator when evaluating loan agreements, during financial reviews, or when assessing the overall financial health of your company.
- The times interest earned ratio calculator is a valuable tool that simplifies this process.
- Automated calculation involves using online calculators or spreadsheet software like Excel to calculate the TIE ratio.
- Its intuitive design and precise calculations provide confidence and ease, making it indispensable for anyone needing accurate financial metrics quickly and easily.
- It is only a supporting metric of the financial stability and cash arm of your business which determines that you have the ability to clear off your liabilities with whatever you earn.
- In a perfect world, companies would use accounting software and diligence to know their position and not consider a hefty new loan or expense they couldn’t safely pay off.
- A low TIE ratio can limit a company’s access to capital, hindering its ability to fund growth or manage unexpected expenses.
Formula and Calculation of Times Interest Earned Ratio
- A consistently high TIE ratio indicates robust financial health, signifying that the company’s earnings comfortably exceed its interest expenses.
- No special calculation is needed—this value comes directly from the company’s financial statements.
- Financial analysts employ the Times Interest Earned (TIE) ratio as a critical tool in their assessment of potential investment opportunities.
- Just ask, and Sourcetable calculates it—displaying results and methodologies directly within the spreadsheet.
- A higher TIE ratio enables a company to take on additional manageable debt, if necessary, without compromising its solvency.
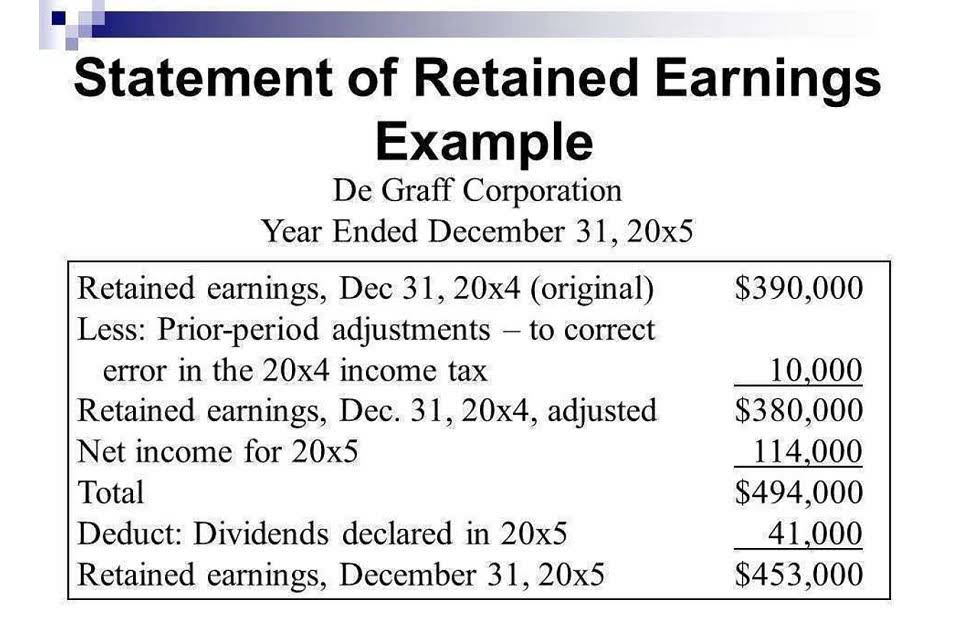
The firm’s overall interest and debt service for a year are amounted to $5,000. To have a detailed view of your company’s total interest expense, here are other metrics to consider apart from times interest earned ratio. Ultimately, you must allocate a percentage for your varied taxes and any interest collected on loans or other debts. Your net income is the amount you’ll be left with after factoring in these outflows. Any chunk of that income invested in the company is referred to as retained earnings. A calculator to determine the times interest earned ratio based on earnings before interest and taxes.
Advantages of Using the Times Interest Earned Ratio Calculator
This includes all interests on bonds, loans, and other forms of financial liabilities. A good TIE ratio is at least 2 or 3, especially in economic times when EBIT can fall due to revenue drops and cost inflation effects. The relatively high TIE ratio means the company’s EBIT is 2 to 3 times its annual interest expense, a margin of safety for the risk of not having enough cash to make interest payments on debt. Financial analysts employ the Times Interest Earned (TIE) ratio as a critical tool in their assessment of potential investment opportunities.
Consider price increases
Non-responsive customers should be sent to collections for contribution margin more follow-up. Understanding why the times interest earned ratio is an essential metric for businesses to make informed decisions. This means that the company has $5 of earnings for every $1 of interest expense. This is a relatively high TIE ratio, which indicates that the company has a strong ability to meet its interest payments. A higher TIE ratio indicates that a company has more earnings available to cover its interest payments, and is therefore less likely to default on its debt.

In that case, it means the company is not generating enough to pay the interest on its loans and might have to dig into the cash reserves, affecting company liquidity. When the times interest earned ratio is too high, it may indicate that cash isn’t being adequately reinvested in initiatives for business growth, which could result in lower future sales. Financial analysts frequently use the TIE ratio for comparative analysis, comparing a company’s TIE ratio against its competitors and industry benchmarks. This relative double declining balance depreciation method assessment provides valuable context regarding a company’s financial position within its sector. A consistently high TIE ratio indicates robust financial health, signifying that the company’s earnings comfortably exceed its interest expenses.
The deli is doing well, making an average of $10,000 a month after expenses and before taxes and interest. You took out a loan of $20,000 last year for new equipment and it’s currently at $15,000 with an annual interest rate of 5 percent. You have a company credit card for random necessities, with a current balance of $5,000 and an annual interest rate of 15 percent.
- Spreadsheet software also allows you to create more sophisticated models to track and analyze the TIE ratio over time.
- The Times Interest Earned Ratio Calculator is a powerful and practical tool for anyone involved in finance, investment, or business management.
- Analysts use the TIE ratio to assess a company’s solvency, specifically its ability to meet its debt obligations.
- The debt service coverage ratio determines if a company can pay all interest and principal payments (also called debt service).
Financial analysts consider it alongside other financial metrics, qualitative factors, and macroeconomic trends to arrive at well-informed investment recommendations. Analyzing the TIE ratio in conjunction with profitability metrics provides a more complete picture of a company’s financial strength. It ensures that debt management is evaluated within the context of overall business performance. Balancing the potential for increased returns with the heightened risk of financial distress is a key consideration for business leaders.
Limitations of the Times Interest Earned Ratio
The debt service coverage ratio determines if a company can pay all interest and principal payments (also called debt service). As economic downturns have a significant impact on all accounting operations of a business, it also possesses the ability to turn a good TIE ratio into a low TIE ratio, which hinders business growth. The onset of recessions, layoffs, demand inelasticity, pandemics, or lower sales and profits could result in much lower EBIT, which would essentially be all of the sales revenue you have earned for a short time period. This means that you will not find your business able to satisfy moneylenders and secure your dividends.

Calculating business times interest earned
It indicates how many times a company can pay off its interest payments from its earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). A higher TIER ratio suggests that a company has a better ability to cover its interest expenses, which is generally considered a positive sign for the company’s financial health. Investors consider it one of the most critical debt ratio and profitability ratios because it can help you determine if times interest earned ratio a company is likely to go bankrupt beforehand. Times interest earned ratio (TIE) is a solvency ratio indicating the ability to pay all interest on business debt obligations.
- TIE is calculated as EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes) divided by total interest expense.
- By understanding the formula and using the calculator effectively, stakeholders can make informed decisions about a company’s ability to meet its interest obligations.
- However, keep in mind that this indicator is not the only way to interpret or size a company’s debt burden (nor its ability to repay it).
- We will also provide examples to clarify the formula for the times interest earned ratio.
- Besides, any bump in the market could make the company non-profitable.
You simply input the EBIT and Interest Expense values, and the calculator automatically computes the TIE ratio. Automated calculation involves using online calculators or spreadsheet software like Excel to calculate the TIE ratio. This method is faster and more accurate, especially when dealing with large datasets or performing multiple calculations. Ultimately, the TIE ratio provides a vital snapshot of a company’s financial health, enabling informed decision-making across the board.




